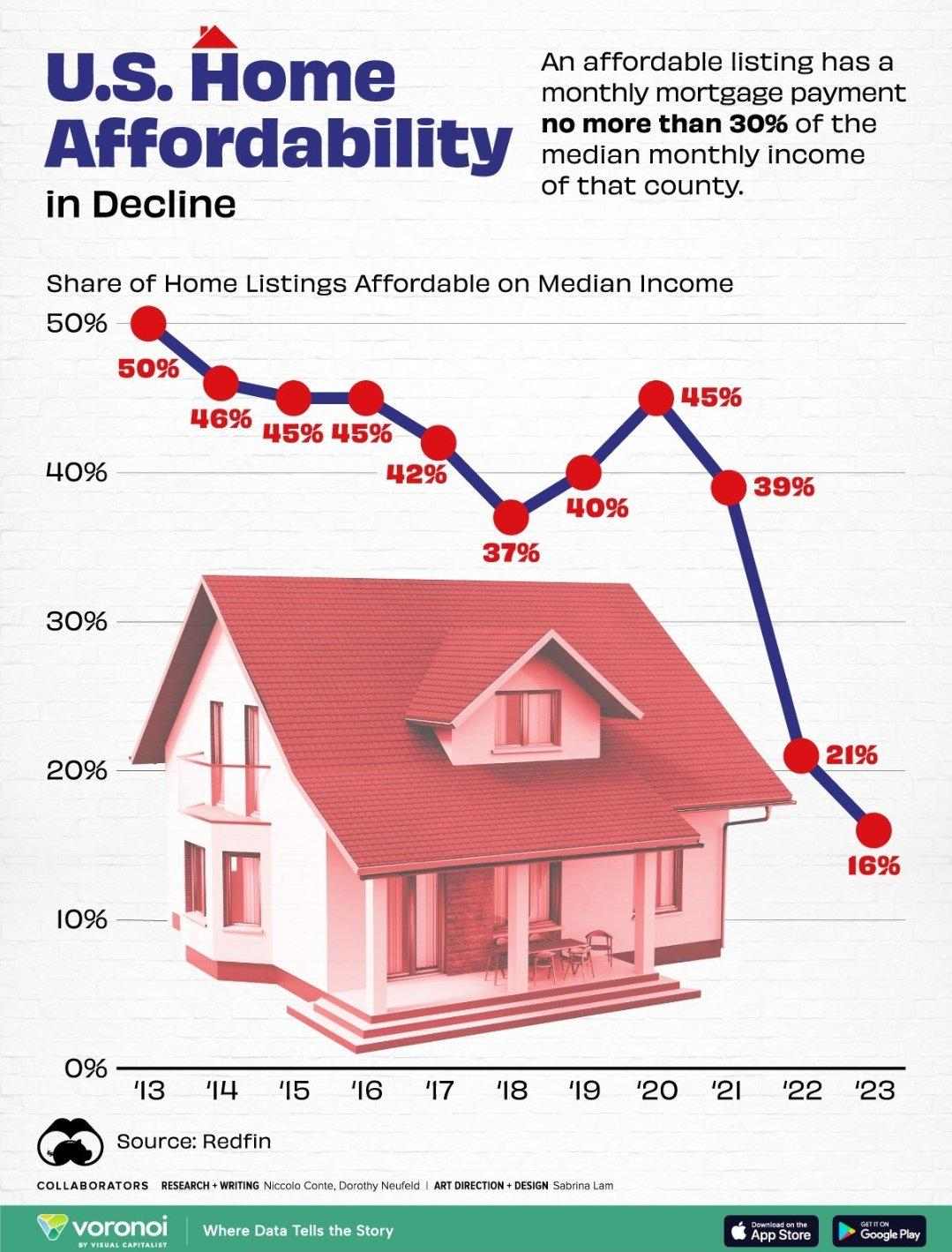
The housing affordability crisis in the United States continues to deepen, leaving many families struggling to secure a place to call home. As housing prices escalate, the challenges are exacerbated by restrictive NIMBY policies, which hinder the construction of new homes and limit supply in an already strained market. Recent housing market analysis suggests that not only rising labor and material costs contribute to this dilemma, but also a significant decline in construction productivity linked to stringent land-use regulations. Without innovative solutions from small builders, who can drive modernization and efficiency in housing development, more Americans will be pushed out of the dream of homeownership. As we delve into this multifaceted issue, it becomes crucial to understand the interplay between these forces and their impact on housing accessibility for future generations.
The current crisis surrounding housing affordability is often characterized by escalating costs and limited options for prospective homeowners. This situation reflects broader economic trends, where local land-use restrictions and regulatory frameworks have significantly affected the ability of builders to meet demand. A close examination reveals how these obstacles have fostered a construction climate less conducive to innovation and productivity, particularly among smaller firms facing greater barriers. As we explore the various dimensions of this issue, it is essential to address the implications of these policies on the housing market and the potential avenues for revitalizing the sector. Understanding the dynamics at play can unlock pathways toward more sustainable solutions that align with the growing needs of communities across the nation.
Understanding the Housing Affordability Crisis
The housing affordability crisis has become a pressing issue for many Americans, affecting not just their ability to purchase homes but also their overall economic stability. As housing prices continue to climb, increasingly outpacing wages and inflation, the dream of homeownership slips away for a significant portion of the population. This crisis is not merely a consequence of economic forces, such as rising labor and material costs, but is also deeply tied to land-use regulations and NIMBY policies that restrict new developments.
Land-use regulations often prioritize local interests over broader community needs, contributing to a scarcity of affordable housing options. Data reveals that between 1970 and 2000, as regulation intensified, construction productivity fell drastically, leading to fewer new homes being built. The failure of local policies to adapt to the growing demand for housing has magnified the crisis, limiting access for first-time buyers and low-income families who are struggling to find affordable options.
The Impact of NIMBY Policies on Housing Development
‘Not In My Backyard’ (NIMBY) sentiments have long been a barrier to housing development in many communities. These policies stifle the construction of new homes by enforcing strict zoning laws and regulations that favor the interests of existing homeowners over potential new residents. NIMBYism results in smaller, bespoke projects that cannot benefit from economies of scale, ultimately driving up costs and reducing the number of affordable housing units that can be constructed.
As it stands, restrictive zoning laws fueled by NIMBY attitudes have led to a lag in housing supply against the increasing demand. With fewer large-scale developments being undertaken, smaller builders, which typically wield less influence and resources, are unable to innovate or drive down costs effectively. This has a cascading effect on the housing market as a whole, amplifying the challenges faced by buyers looking for affordable housing solutions.
Analyzing Construction Productivity Decline
Research indicates that construction productivity in the United States has experienced a dramatic decline since the 1970s. Initially, the building sector was more productive and could scale quickly to meet housing demands. However, with the advent of stringent land-use regulations and increased NIMBY sentiments, productivity has stagnated. The shift towards smaller projects means that fewer homes are built per worker, which translates directly into higher costs for consumers.
This decline is alarming when juxtaposed with other industries that have seen substantial efficiency gains over the same period. The construction sector’s lagging productivity not only impacts the availability of housing but also threatens the overall economy by limiting job creation and innovation in construction methods. Addressing this decline involves reassessing regulations that inhibit large-scale developments, which can foster an environment for improved productivity and affordability.
Land-Use Regulations: A Barrier to Innovation
The intersection of land-use regulations and housing construction reveals a complex barrier to innovation within the industry. As developers grapple with varying local zoning laws, they find themselves constrained, unable to pursue innovative building practices or technologies that could lower costs. This regulation-induced homogenization of development has stifled creativity in design and construction methods, exemplifying how policy can shape the landscape of housing availability.
Moreover, the focus on individualized projects, constrained by local demands, limits the implementation of modern construction techniques that could revolutionize the market. As the industry fails to innovate, it misses out on opportunities to enhance construction speeds and reduce expenses, further entrenching the affordability crisis. A more flexible approach to land-use regulations could stimulate the sector, inviting creativity and efficiency back into a critical element of the economy.
Small Builders and Market Dynamics
Small builders often face unique challenges within a heavily regulated housing market characterized by NIMBY sentiments and stringent land-use policies. Unlike larger firms, these builders tend to have fewer resources and less clout in navigating complex regulatory environments. As a result, they are often unable to compete effectively, which can stifle their ability to innovate or pursue larger, more cost-efficient projects that could alleviate the housing shortage.
The decline in small builders has significant implications for the housing market. As larger builders dominate, the diversity of housing options shrinks, leading to a less competitive marketplace. This can result in higher costs for consumers as specialized and customized homes become the norm rather than mass-produced, affordable options. Empowering small builders through streamlined regulations could inject new vitality into the housing sector, promoting innovation and ultimately increasing affordability.
The Role of Housing in Economic Growth
Housing is a pillar of economic growth, providing stability not just for families but also for local communities and the broader economy. As construction slows and housing becomes less affordable, the ripple effects can stall economic development. When families spend a disproportionate amount of their income on housing, they are left with less to invest in other areas of the economy, which can curb overall economic vitality.
Conversely, a thriving housing sector can stimulate job growth and innovation, creating a positive feedback loop that enhances economic robustness. Policymakers and community leaders must recognize the integral role that affordable housing plays in fostering economic growth. By working to undo restrictive land-use regulations and enabling a diverse array of housing types, they can pave the way for a more prosperous future.
Examining Long-Term Housing Trends
Long-term housing trends reveal critical insights into the evolving dynamics of the market. Over the past few decades, there has been a significant shift in the types of homes being constructed and who is able to afford them. The decline in large-scale housing projects has resulted in higher costs and less availability, further complicating the landscape of homeownership for younger and low-income individuals.
Analyses show that the predilection for smaller, more localized projects has not only escalated costs but also widened the gap between homeownership and rental markets. This trend necessitates a reassessment of housing policies to incorporate strategies that promote increased supply, especially in areas where demand is strongest. Recognizing these patterns will be crucial in developing solutions that address the affordability crisis and promote equitable access to housing.
Innovative Solutions for Housing Affordability
As the housing affordability crisis deepens, the call for innovative solutions becomes more urgent. One promising avenue involves embracing new construction technologies and methodologies that streamline processes and reduce costs. By integrating advances in prefabrication, modular building, and sustainable practices, the housing industry can respond more effectively to market demands while maintaining environmental responsibilities.
Moreover, collaboration between policymakers, industry leaders, and local communities is essential to foster an environment conducive to innovation. Redesigning land-use policies to prioritize development and incentivize larger projects could unlock the potential for affordable housing solutions. By thinking creatively and embracing new models, the housing sector can begin to heal the affliction of affordability and accessibility.
Intergenerational Wealth and Housing Equity
The gap in housing wealth between generations underscores the importance of equitable access to housing. As older generations continue to benefit from increased home equity, the younger population finds themselves sidelined, struggling to enter the housing market. This disparity not only highlights issues of equity but also raises questions about the long-term stability of the housing market and its effects on social mobility.
Addressing intergenerational wealth transfer requires a comprehensive approach to housing policy, one that promotes affordability and accessibility across demographics. Stabilizing homeownership opportunities for younger individuals can mitigate wealth disparities and foster a healthier economy. As communities prioritize inclusive housing practices, they pave the way for a more equitable future where homeownership is within reach for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do NIMBY policies impact the housing affordability crisis?
NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies often lead to stricter land-use regulations that limit housing construction, contributing to the housing affordability crisis. These restrictions prevent builders from utilizing economies of scale, resulting in higher housing costs and fewer homes being built overall.
What role do land-use regulations play in the housing affordability crisis?
Land-use regulations play a significant role in the housing affordability crisis by constraining the development of new housing projects. These regulations often impose costly and time-consuming requirements on builders, which can drive up prices and limit the availability of affordable housing.
How can housing market analysis help address the housing affordability crisis?
Housing market analysis is essential in understanding the dynamics of supply and demand in the housing market. By identifying trends, such as construction productivity decline and the impact of NIMBY policies, stakeholders can devise strategies to alleviate the housing affordability crisis.
Why has construction productivity declined in relation to the housing affordability crisis?
The construction productivity decline is closely tied to the housing affordability crisis. As land-use regulations have increased, builders face greater challenges in launching large-scale projects. This has led to smaller, less efficient construction firms that struggle to innovate and produce affordable housing.
What innovations are small builders adopting to combat the housing affordability crisis?
Small builders are increasingly focusing on innovation to combat the housing affordability crisis by utilizing new construction technologies, adopting modular building techniques, and implementing cost-saving measures. However, they often face limitations due to existing NIMBY policies and stringent land-use regulations.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Housing Costs | The price of a new single-family home has doubled since 1960, driven by factors such as labor and material costs. |
| NIMBY Land-Use Policies | “Not In My Backyard” (NIMBY) policies contribute to rising housing costs by imposing restrictions that limit the scale of housing developments. |
| Decline in Construction Productivity | From 1970 to 2000, productivity in the construction sector decreased by 40% despite growth in the overall economy. |
| Impact of Large-Scale Builders | Large firms producing homes have a productivity advantage, producing four times more units per employee compared to smaller firms. |
| Intergenerational Wealth Transfer | A significant decline in housing wealth has been noted among younger generations compared to older homeowners. |
| Innovation in Construction | The construction industry has seen decreased patenting and innovation since the 1970s compared to other sectors. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis is significantly influenced by factors such as zoning and land-use regulations, which stifle innovation and productivity in the construction sector. As a result, new homes have become prohibitively expensive for many Americans, particularly younger generations. The reliance on small-scale projects driven by NIMBYism hampers the potential for mass production, leading to soaring costs and a lack of affordable options. Addressing the housing affordability crisis will require a reevaluation of these policies to promote sustainable, large-scale development that meets the needs of all citizens.